https://www.ancienthistorylists.com/people/7-homo-species-close-present-human-existed-earth/
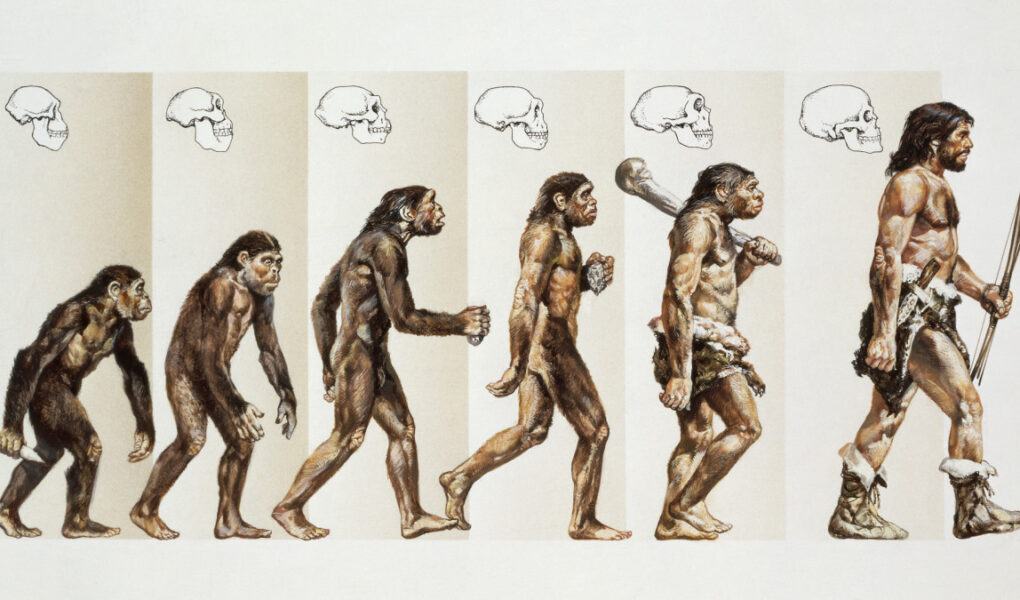
The Earth has a 4.6-billion-year history. However, Homo sapiens (modern humans) only evolved between 400,000 and 250,000 years ago. Humans evolved from the family hominid (great apes) that have existed on Earth for around 20 million years. Over time, different human species with different characteristics have existed on Earth, but not all species of humans have survived the journey with many of them becoming extinct. The only human species left is Homo sapiens.
The idea of humans being linked to the apes came after the publication of Charles Darwin’s On the Origin of Species in 1859. He was the first to point out that every species has emerged from an earlier one. Later, two scientists, Thomas Huxley and Richard Owen, supported him. Huxley published a book in 1863 entitled Evidence as to Man’s Place in Nature. Even though scientists held several views and theories, the major problem was proof because there was a lack of fossil intermediaries. Eugène Dubois discovered the first fossil intermediary in 1891 at Trinil in the Dutch East Indies (modern-day Indonesia) proving that there were species between humans and apes. He called his finding Pithecanthropus erectus or Java Man. Additional fossils were discovered in Africa in 1920 and the study of the evolution of humans began thereafter. Here is the list of seven Homo species that have existed on Earth:
7. Homo Heidelbergensis

Homo heidelbergensis lived on Earth between 700,000 and 200,000 years ago. They emerged from Africa. The Homo heidelbergensis male was about 5ft 9in (175cm) tall and weighed around 136lbs (62kg), whereas the female average height was 5ft 2in (157cm) and with a weight of 112lbs (51kg). They had a large brain case with a flatter face than today’s humans. They were the first human species to adapt to colder climates and to build their own shelters to live in. They were also widely known for their ability to hunt large animals, which had not been seen in human species before them.https://f071c7aa246d99b13a90d8f6b54315eb.safeframe.googlesyndication.com/safeframe/1-0-38/html/container.html
The first Homo heidelbergensis fossil was discovered on October 21, 1907, by a worker in Germany. The workman handed it over to Professor Otto Schoetensack from the University of Heidelberg who later identified and named the fossil.
6. Homo Rudolfensis

Homo rudolfensis is another extinct species that falls into the hominid category. They are believed to have lived around 1.9 million to 1.8 million years ago. Their physical build, weight, and height is still unknown due to the scarcity of cranial fossils.
Paleoanthropologist Meave Leakey and her team announced the discovery of a face and two jawbones belonging to Homo rudolfensis on August 8, 2012. The fossil known as KNM-ER 1470 was at the center of a debate about its age. It was first thought to be around three million years old but later this was corrected to 1.9 million.
The difference in the skull from other Homo species led to the creation of a new species called Homo rudolfensis. There are certain features of the ER 1470 to suggest that it is no different from other Homo species such as the lack of heavy muscle, the crests of australopithecine crania, and the smoothly rounded occipital bone similar to that of Homo erectus. However, other key features suggest that Homo rudolfensis are different from other Homo species having much longer faces with the upper part being narrower than the middle, and with many more megadont postcanines.
5. Homo Habilis
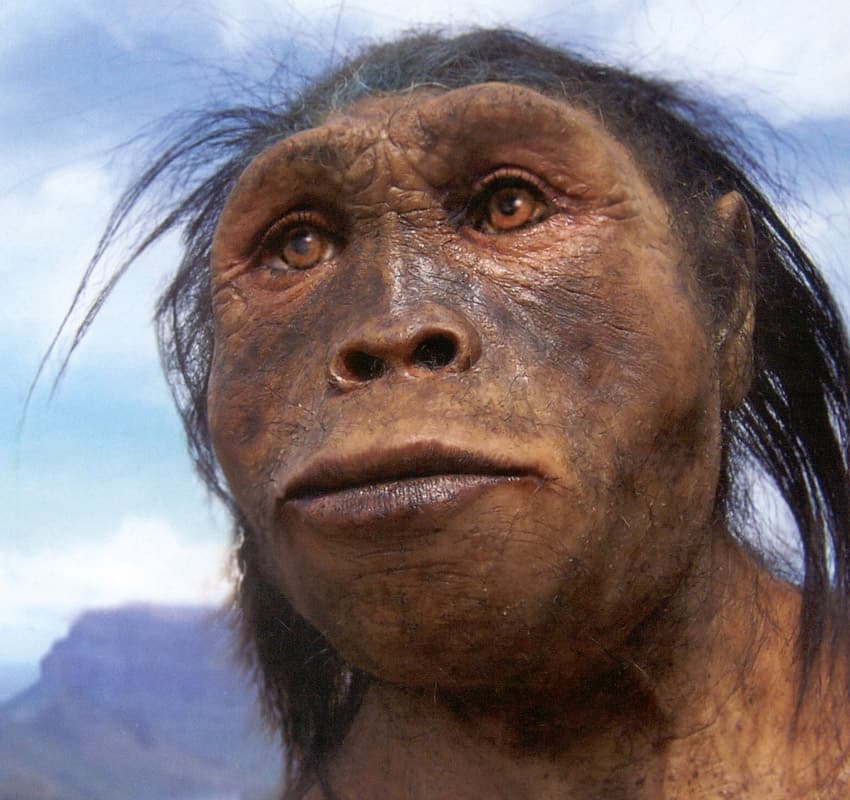

Homo habilis was another species of hominids who lived on Earth between 2.4 and 1.4 million years ago. Homo habilis possessed some ape-like features such as long arms and a moderately prognathic face. They had a larger brain case in the range of 550cm to 687cm. However, they had a smaller face and smaller teeth. There has been some debate as to whether Homo habilis should be classified as Homo since they had very few characteristics of other Homo species, but scientists discovered that they had the capacity to use stone tools for various purposes.
There are three key fossils available of Homo habilis: KNM-ER 1813, OH 24, and OH 8. The first fossil was found by the scientists Louis and Mary Leakey at Olduvai Gorge in Tanzania in the 1960s.
4. Homo Floresiensis
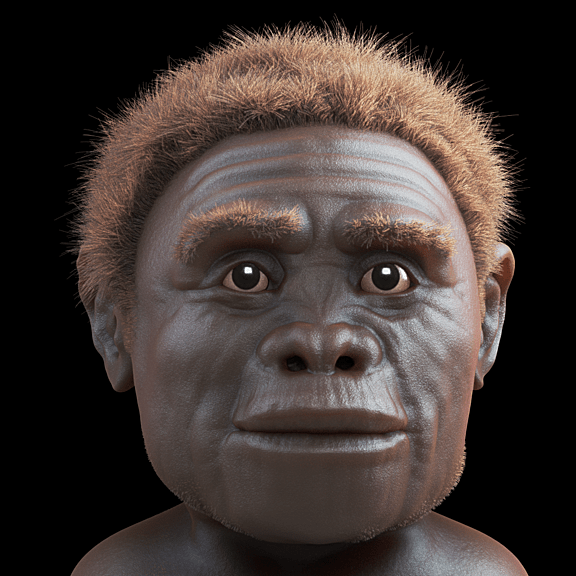

Homo floresiensis was believed to have lived from 95,000 to 17,000 years ago in Indonesia. They were quite small in size, around 3.5 feet, with a tiny brain. There is evidence that Homo floresiensis made stone tools and used to hunt small elephants and large rodents.
The key fossils of Homo floresiensis were found in 2003 in Indonesia and were named LB-1. The female head was a third of the size of a modern human brain. Perhaps their small bodies enabled them to survive on the small island with limited resources.
3. Homo Erectus
Homo erectus is an extinct species of early human that lived throughout the Pleistocene period from about 1.9 million years to most recently 143,000 years ago. The first Erectus fossil was discovered in Java (present-day Indonesia) in the early 1890s by Eugène Dubois. The study of the fossil proved that Homo erectus originated in Africa and spread through India, China, Georgia, and Java.
Homo erectus were generally in the range of 4 feet 9 inches to 6 feet 1 inch with a weight of around 88 to 150lbs. Their height and weight were different from the fossils found in other parts of the world. The fossils from Africa had a larger body size than those of Indonesia, China, and Georgia. Their elongated legs and short arms helped them climb trees easily and run faster than modern-day human beings.
2. Homo Neanderthalensis

Neanderthal is an extinct species of human with the closest similarity to modern humans. Only 0.12 percent of their DNA is different to modern humans. The Neanderthal was believed to have existed from about 600,000 to 30,000 years ago, and lived throughout Europe and southwest to central Asia. They had most of the features of modern humans, they used different tools for hunting, and wore symbolic ornamental objects. There is evidence that they used to bury their dead with offerings such as flowers. Some earlier human species have also been found to have engaged in such symbolic behavior.
A study has indicated that the Neanderthal and the modern human brain were similar at birth. However, in adulthood, their brains became larger. They were stronger than modern humans with a huge body size: male (164-168cm) and female (156-158cm).
1. Homo Sapiens
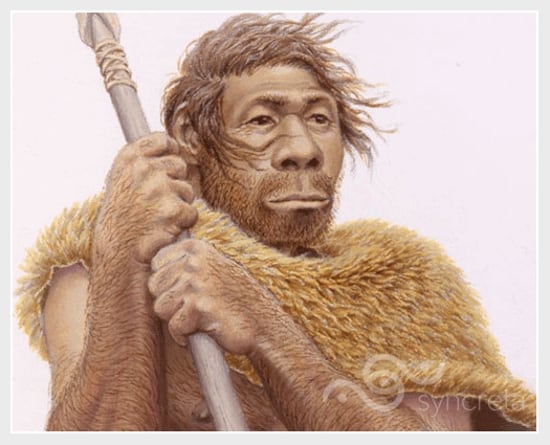

Most hominid species that existed on Earth became extinct during climatic changes but Homo sapiens survived and became the ancestors of modern humans. Homo sapiens lived together, hunted food, and evolved to such an extent that they could cope with the climatic changes that occurred. Besides hunting, they discovered how to propagate certain plants and how to breed animals, which changed history forever. Soon they learned to produce more food, and ate a variety of animals and plants. Their control over fire and their tendency to live in larger groups also led to the creation of better shelters.
Scientists have found various fossils that support strong evidence of Homo sapiens. The oldest known fossils were discovered in Herto, Ethiopia. Researchers from the University of California found the skulls of two adults and a child, who lived around 160,000 to 40,000 years before modern times.